The differences between turbocharged and naturally aspirated engines available in sales
Exploring the Differences Between Turbocharged and Naturally Aspirated Engines
Exploring the Differences Between Turbocharged and Naturally Aspirated Engines
Navigating the world of engines brings us to the distinction between turbocharged and naturally aspirated powertrains. In this blog post, we’ll delve into a comprehensive review of the differences between these two engine types, shedding light on their respective strengths, characteristics, and the implications they hold for potential buyers seeking the ideal power source for their vehicles. Exploring the Differences Between Turbocharged and Naturally Aspirated Engines
Understanding Turbocharged and Naturally Aspirated Engines
1. Turbocharged Engines
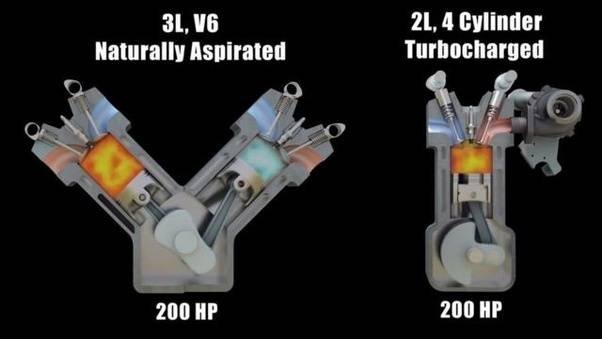
Turbocharged engines utilize a forced air induction system enabled by a turbine-driven forced induction device, or turbocharger, to enhance engine power output. This technology allows smaller engines to produce power outputs comparable to larger naturally aspirated engines, providing increased efficiency and performance. Exploring the Differences Between Turbocharged and Naturally Aspirated Engines
2. Naturally Aspirated Engines
Naturally aspirated engines rely solely on atmospheric pressure to intake air into the engine. These engines typically have larger displacements to generate power, offering a linear power curve and consistent performance across a wider range of engine speeds. Exploring the Differences Between Turbocharged and Naturally Aspirated Engines
Performance and Power Delivery
1. Turbocharged Engines
Turbocharged engines are known for their ability to deliver enhanced power and performance, especially at higher altitudes. The forced induction provided by the turbocharger enables these engines to generate more power without significantly increasing engine displacement.
2. Naturally Aspirated Engines
Naturally aspirated engines offer a more consistent power curve across the engine’s RPM range, providing linear power delivery and predictable performance. While lacking the immediate power surge of turbocharged engines, they provide reliable and consistent power output. Exploring the Differences Between Turbocharged and Naturally Aspirated Engines
Fuel Efficiency and Environmental Impact
1. Turbocharged Engines
Due to their smaller displacement and forced induction, turbocharged engines can offer increased fuel efficiency, especially when driven conservatively. However, under heavy load or when utilizing the turbocharger’s full potential, fuel efficiency may decrease.
2. Naturally Aspirated Engines
Naturally aspirated engines tend to offer a more predictable fuel consumption pattern, providing relatively consistent efficiency, particularly during steady-state or low-speed driving conditions. However, at higher RPMs, fuel efficiency may decrease compared to turbocharged equivalents. Exploring the Differences Between Turbocharged and Naturally Aspirated Engines
Engine Size and Weight
1. Turbocharged Engines
Turbocharged engines can produce higher power outputs with smaller displacements, resulting in a more compact and lightweight powertrain. This can contribute to a lighter overall vehicle weight and better weight distribution.
2. Naturally Aspirated Engines
Naturally aspirated engines, due to their larger displacement and size to achieve similar power outputs compared to turbocharged engines, may result in a heavier powertrain and a slightly heavier overall vehicle.
Maintenance and Longevity
1. Turbocharged Engines
Turbocharged engines may require more intricate maintenance due to the added complexity of the forced induction system. However, with appropriate care, these engines can offer long-term reliability and durability.
2. Naturally Aspirated Engines
Naturally aspirated engines, with their simpler design and less complex induction systems, may require less frequent maintenance. Their robust design and consistent power delivery contribute to their renowned longevity. Exploring the Differences Between Turbocharged and Naturally Aspirated Engines
Cost Considerations and Market Availability
1. Turbocharged Engines
While turbocharged engines can offer compelling performance and efficiency benefits, they often come with a higher initial purchase price. However, advancements in technology have made turbocharging more common across various vehicle categories and price points.
2. Naturally Aspirated Engine
Naturally aspirated engines, being a traditional and widely used engine type, are often more readily available and can be found across a diverse range of vehicles. Their familiarity and widespread use contribute to their accessibility and favorable pricing. Exploring the Differences Between Turbocharged and Naturally Aspirated Engines
Conclusion: Navigating Engine Choices
Understanding the differences between turbocharged and naturally aspirated engines is pivotal when choosing the ideal power source for a vehicle. While turbocharged engines offer enhanced power and potential efficiency benefits, naturally aspirated engines provide consistent power delivery and a straightforward maintenance profile. Depending on specific needs, preferences, and driving habits, either option can deliver a rewarding and reliable driving experience. Consulting with a knowledgeable professional when selecting an engine can provide valuable insight and help align engine choice with individual requirements.
By comprehending the distinctions between these engine types, potential buyers can effectively evaluate the trade-offs and make informed decisions, ensuring the engine they choose aligns with their distinctive goals and preferences. Exploring the Differences Between Turbocharged and Naturally Aspirated Engines
We trust you’ll find this comprehensive review-driven blog post on the differences between turbocharged and naturally aspirated engines enlightening and informative! If you need further details or adjustments, feel free to reach out. Exploring the Differences Between Turbocharged and Naturally Aspirated Engines
Yanmar 8LV Diesel Marine Engines